Biodiversity
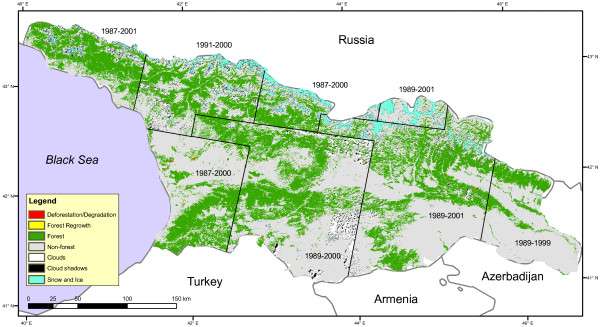
Over the last 50 years, nature has changed unprecedentedly around the world, due to the acquisition of natural areas, the extraction of living organisms, climate change, pollution, and invasive alien species. The increase in the consumption of biological resources is accompanied by a decrease in the sustainability of natural environmental regulation. The number of endangered species of plants and animals is rapidly increasing. According to the latest estimates 46, the tendency to lose biodiversity and ecosystem services will continue to deteriorate even if current practices in energy, food, water supply, and resource use are not changed. Nature can be preserved and preserved while achieving social goals and improving the quality of life, but this requires immediate and effective efforts at local, national and global levels.
Why is Georgia’s Biodiversity Conservation Important?
Due to the diversity of species and habitats, the high level of endemism and the spread of ecosystems of global importance, the territory of Georgia is included in the priority list of nature conservation 47.
However, due to significant threats to biodiversity, our country is also part of the world’s biodiversity hotspots 48;
Georgia’s biodiversity is at significant risk of degradation and degradation of natural habitats, excessive use of natural resources, environmental pollution, invasive alien species, and climate change;
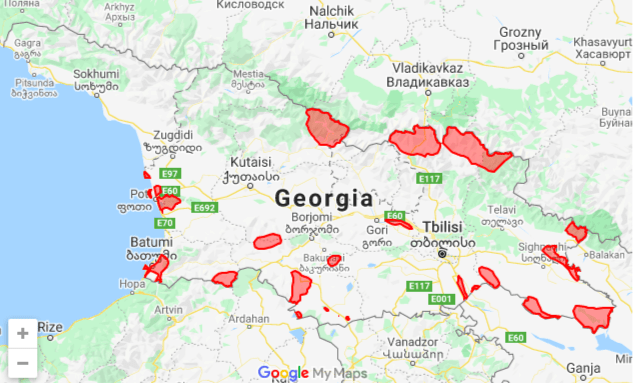
Georgia has been in the process of establishing an emerald net since 2009, with the aim of protecting the species by preserving their habitats. In 2017-2018, Emerald Territory was granted 39 territories with a total area of 841 875.5 ha. Along with the candidate and proposed areas, the total area of the emerald is 1 285 974.74 ha, which is 18.45% of the total territory of Georgia.