Geography
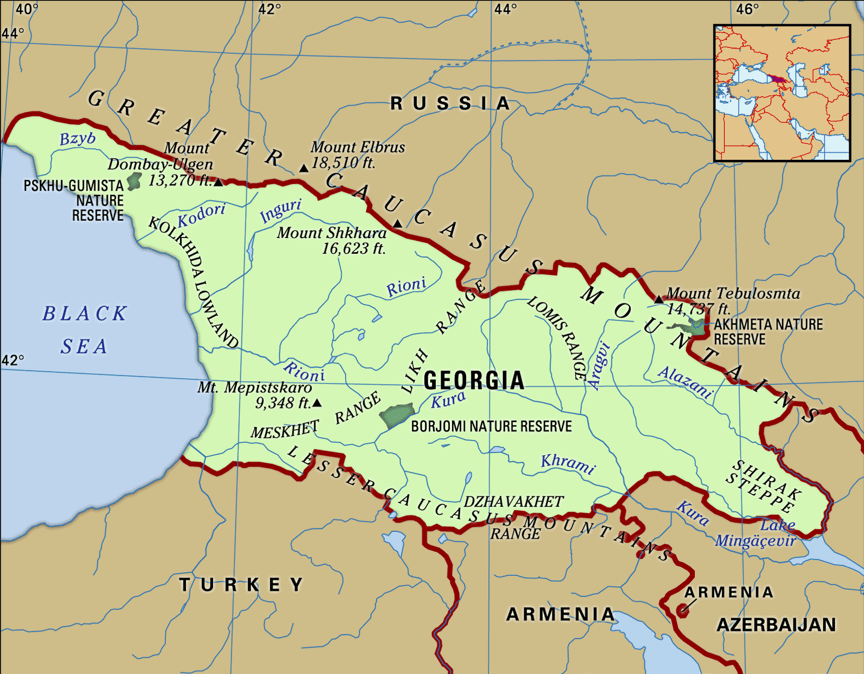
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region, on the coast of the Black Sea. Sometimes considered a transcontinental country, it is located at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, and is today generally regarded as part of Europe. It is bordered to the north and northeast by to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan.
Georgia is largely surrounded by the Greater Caucasus and Lesser Caucasus mountains, which form part of a natural boundary between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Because the Europe—Asia boundary is essentially a “historical and cultural construct”, Georgia’s continental placement has varied greatly. Anaximander placed the boundary between Europe and Asia along the River (the modern Rioni River), which effectively located northern parts of Georgia in Europe and the south in Asia, a convention also followed by Herodotus. According to one 18th century definition, which set the Kuma—Manvch Depression as the continental boundary, Georgia and the entire Caucasus fell into Asia. However, yet other definition drew the line at Aras River effectively placing all of Georgia in Europe.
Notwithstanding variations in geographic placement, Georgia’s proximity to the bulk of Europe, combined with various historical, cultural and political forces, has led increasingly to its inclusion in Europe. The country has joined European organizations, such as the Council of Europe and Eurocontrol, and has been deemed eligible to apply for membership of the European Union if it so wishes in the future
Coastline
The coastline of Georgia is 310 km long. Out of the Georgian coastline, 57 km is the coastline of Ajaria (Ajara), and 200 km is the coastline of Abkhazia.L The Encyclopedia of the Nations lists the total length of the coastline as 315 km long. Georgia has an Exclusive Economic Zone of 21,946 km2 (8,473 sq mi) in the Black Sea.